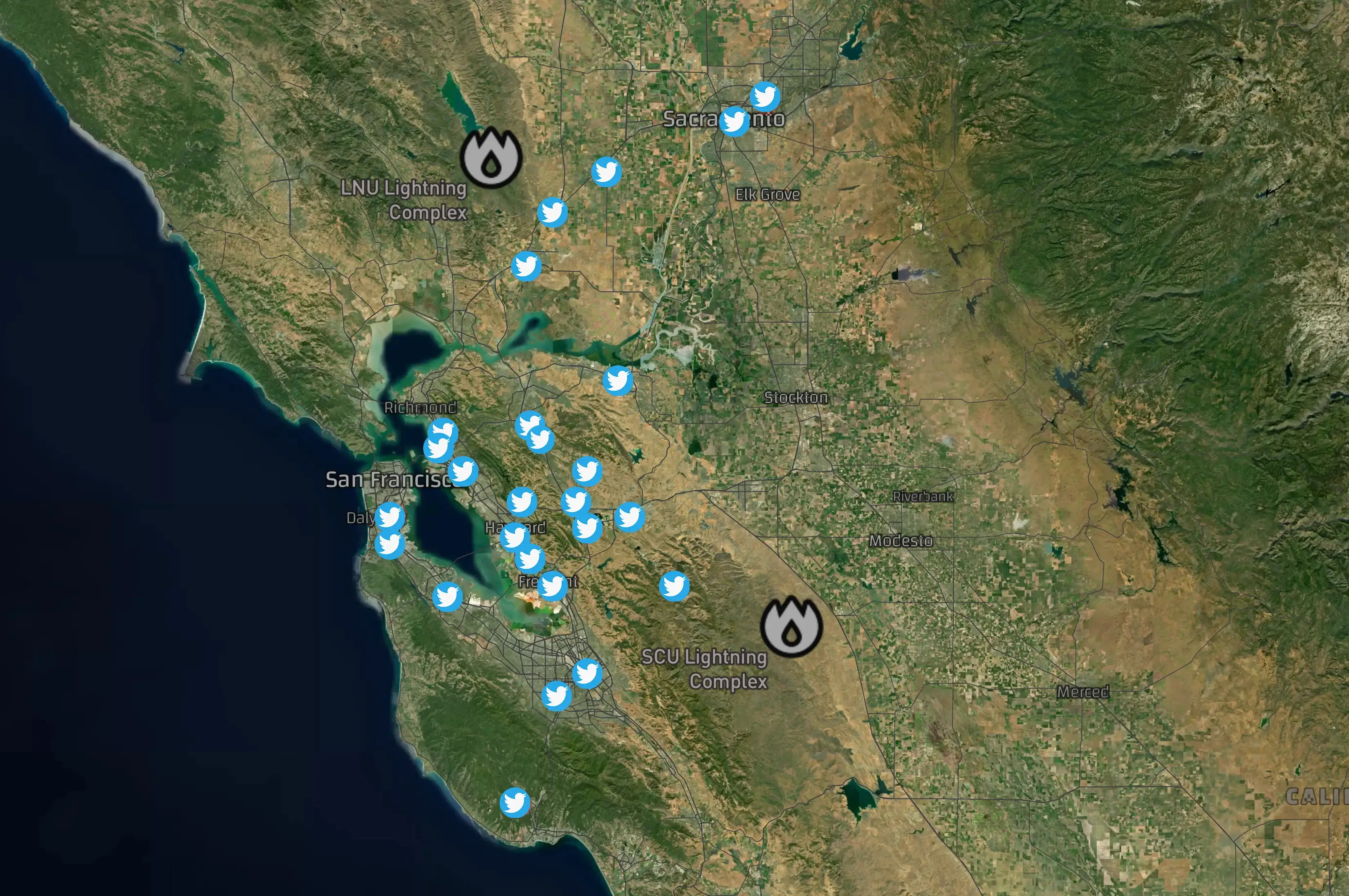
To illustrate the power of social media data, we analyzed the data for two massive 2020 wildfires:
The SCU Lightning Complex began on August 16, 2020, and the LNU Lightning Complex ignited a day later on August 17, 2020. We conducted an analysis of social media messages during the onset of these wildfires. Below is a map of the early messages that identified the starting fires. Users were mentioning smoke, ashes, and even visible fires.
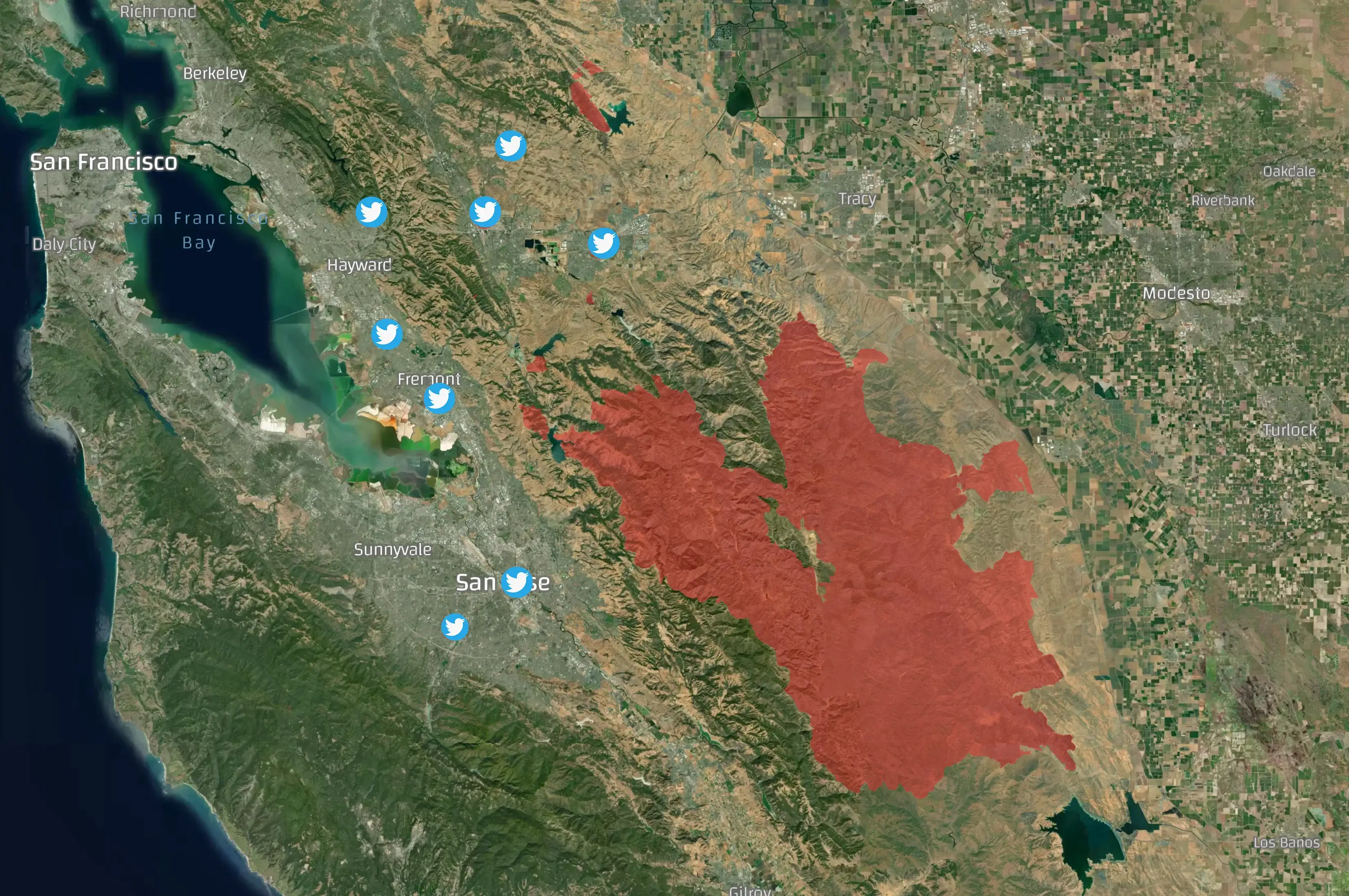
SCU Lightning Complex
On August 16, 2020, at approximately 9:25 AM, as reported by CAL FIRE, the SCU Lightning Complex fires began. The Geotagging AI models were able to capture the early tweets in which users located in the surrounding urban areas started mentioning fire and smoke. Below are examples of such tweets.


The SCU Lightning Complex became one of the largest wildfires of the devastating 2020 California wildfires season, scorching a staggering 396,624 acres of land. This fire originated from multiple fire incidents ignited by lightning strikes in three distinct areas: the Canyon Zone, the Calaveras Zone, and the Deer Zone. Eventually, these fires merged into a single massive fire. The aforementioned example tweets serve as early indicators, specifically for the Canyon Zone in Alameda County.
The map below showcases the extensive fire perimeter of the SCU Lightning Complex fires, which spanned across expansive forested regions. It also depicts the locations of the initial social media signals originating from nearby urban areas.
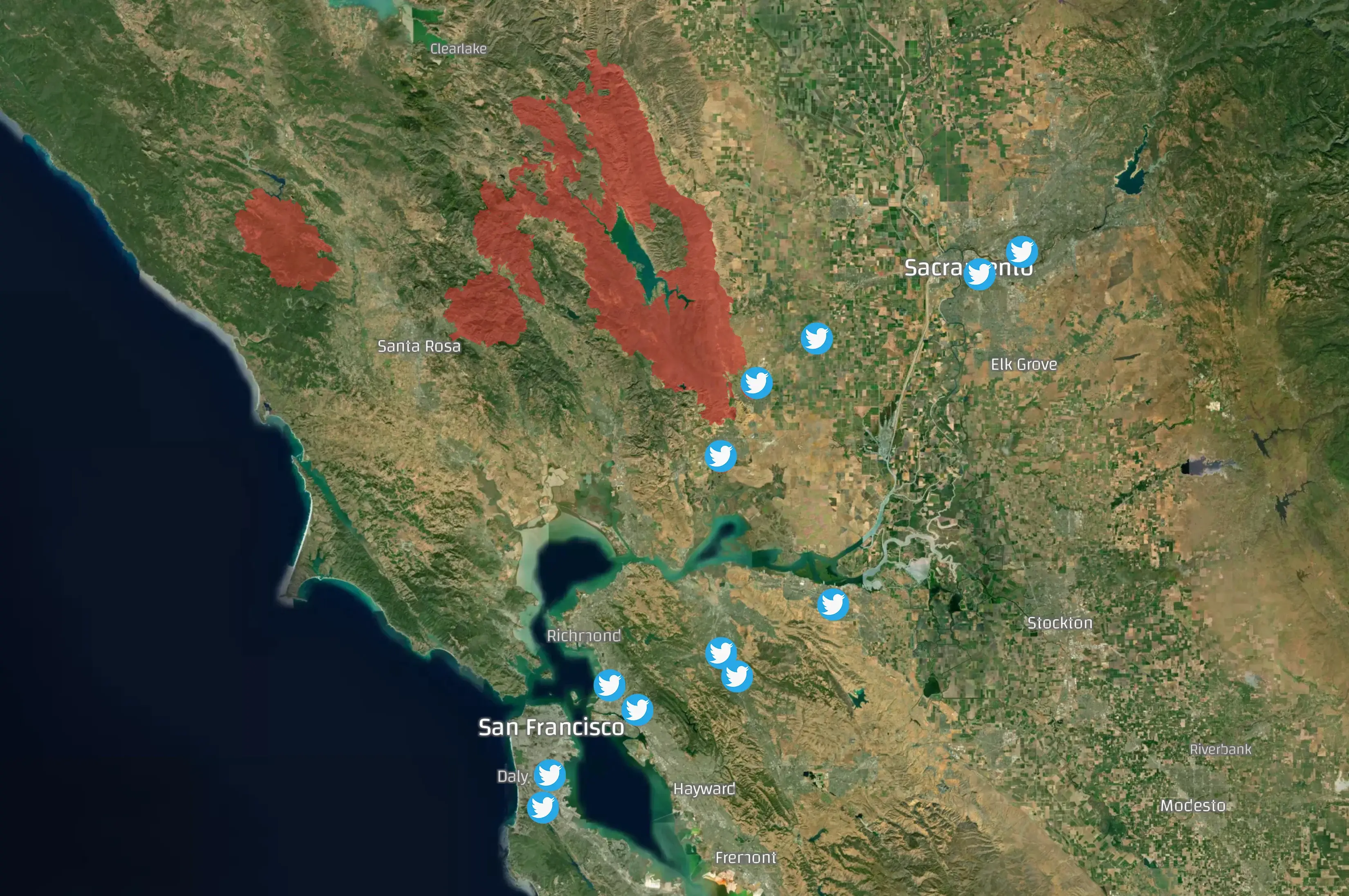
LNU Lightning Complex
A day later, the LNU Lightning Complex fires started at around 8 AM. The Geotagging AI again captured early tweets in which users identified the starting fire.


The LNU Lightning Complex fires is a large complex of wildfires that burned 363,220 acres of land across Lake, Napa, Sonoma, Solano, and Yolo Counties. The fires resulted in 6 fatalities and 5 people injured.
Displayed in the map below are the fire perimeter and the locations of tweets that indicated early signs of wildfires. While the wildfires eventually consolidated into a massive blaze, they originated as discrete ignited flames. This is reflected in the distribution of the locations of social media messages within nearby urban areas.
Combined with sophisticated Natural Language Processing techniques, Geotagging AI data is a valuable information source for detecting wildfires at the early stages. This data provides extensive coverage of and serves as an early alerting system for wildfires, supporting first responders in their efforts to promptly react, mitigate and alleviate the adverse effects of wildfires.



